Cardiac tamponade is a cardiac emergency and can be fatal if it is not quickly diagnosed and treated promptly. In adults, cardiac tamponade appears to be slightly more common in men than in women.
, Cardiac tamponade occurs when too much fluid collects in the pericardium (the sac around your heart). Their case histories are presented and the management in the light of these described.
 Cardiac tamponade BY PANKAJ From slideshare.net
Cardiac tamponade BY PANKAJ From slideshare.net
The fluid may collect slowly or quickly, and puts pressure on your heart. Published online by cambridge university press: This results in “bowing” of the intraventricular septum into the left ventricle causing a reduction in left ventricular filling. Clinical sings of cardiac tamponade depends on the rapidity of the fluid accumulation and on the fluid.
Cardiac tamponade BY PANKAJ Ut southwestern’s skilled heart doctors use a variety of.
In adults, cardiac tamponade appears to be slightly more common in men than in women. Prompt diagnosis is key to reducing the mortality risk in patients with tamponade. Cardiac tamponade is the accumulation of excess fluid within the pericardial space, resulting in impaired cardiac filling, reduction in stroke volume, and epicardial coronary artery compression with resultant myocardial ischemia. If not treated, it is always fatal.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Cardiac tamponade is a cardiac emergency and can be fatal if not diagnosed and treated quickly.anyone who experiences an acute onset of chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, and a feeling of drowsiness should call 911 immediately. The acute onset of these symptoms could indicate the early stages of pericardial effusion,. Manage your other health conditions: Management of cardiac tamponade after cardiac surgery. Cardiac Tamponade Pathophysiology, Etiology, Symptoms, Diagnosis and.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cardiac tamponade is a fluid buildup around the heart that constitutes a medical emergency. Cardiac tamponade can appear acutely, or it may develop rather gradually. The fluid that causes tamponade is usually either a typical pericardial effusion (that is, the accumulation of an abnormal amount of fluid in the pericardial sac) or bleeding into the pericardial sac. Factors that influence the management strategy include evaluating the cause, providing haemodynamic support, and. Cardiac tamponade.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Cardiac tamponade occurs when too much fluid collects in the pericardium (the sac around your heart). This concept is seen clinically in the form of “pulsus paradoxus.”. Cardiac tamponade has the following symptoms: In either case, symptoms are usually quite striking, and the resolution of symptoms requires the. The “3 D’s” Cardiac Tamponade (Beck’s Triad) Cardiovascular Care.
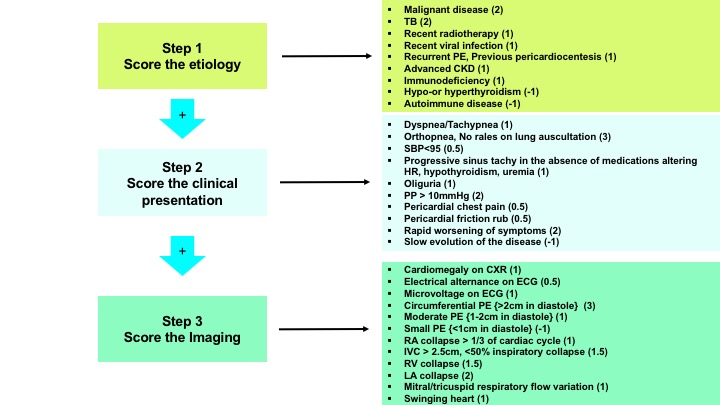 Source: recapem.com
Source: recapem.com
Cardiac tamponade is an uncommon problem in a district general hospital. Factors that influence the management strategy include evaluating the cause, providing haemodynamic support, and. Trauma and certain diseases can cause cardiac tamponade. Prompt diagnosis is key to reducing the mortality risk in patients with tamponade. Cardiac Tamponade cardiac tamponade RECAPEM RecapEM.
 Source: prognosisapp.com
Source: prognosisapp.com
Stabbing pain in the chest, abdomen, shoulder or back. Cardiac tamponade happens when the space around your heart fills with blood or other fluid, putting pressure on your heart. Cardiac tamponade is a cardiac emergency and can be fatal if it is not quickly diagnosed and treated promptly. Learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment of cardiac tamponade. Cardiac Tamponade.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cardiac tamponade has the following symptoms: When the ventricles are not allowed to fill as they want, we see a decrease in stroke volume, a drop in cardiac output, and visible signs of shock. This fluid quickly compresses the heart, preventing it from adequately pumping blood because it cannot fill properly. The blood or fluid puts extra pressure on the heart. Cardiac tamponade BY PANKAJ.
 Source: picturingmedicine.com
Source: picturingmedicine.com
Stabbing pain in the chest, abdomen, shoulder or back. In certain conditions, fluid removal is still the optimal choice, but a conservative approach using haemodialysis may be employed. Cardiac tamponade is a buildup of fluid in the pericardial sac that surrounds the heart which impairs the heart’s ability to contract and the ventricles to fill normally. This makes it difficult for your heart to pump. Picturing Medicine Trauma.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Some of the symptoms of cardiac tamponade might look like other health problems. Variants include low pressure (occult) and regional cardiac tamponade. Cardiac tamponade is an emergency, and definitive therapy is fluid removal by pericardiocentesis. Triage strategy for urgent management of cardiac tamponade: Cardiac tamponade gk.
 Source: lecturio.com
Source: lecturio.com
The cardiac tamponade triad presents with hypotension, a narrow pulse pressure, jvd, muffled heart sounds and potentially pulsus paradoxus. Cardiac tamponade is an uncommon problem in a district general hospital. Cardiac tamponade is a cardiac emergency and can be fatal if not diagnosed and treated quickly.anyone who experiences an acute onset of chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, and a feeling of drowsiness should call 911 immediately. In either case, symptoms are usually quite striking, and the resolution of symptoms requires the. Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade Concise Medical Knowledge.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Cardiac tamponade is a health problem affecting the heart. Manage your other health conditions: Stabbing pain in the chest, abdomen, shoulder or back. The fluid may collect slowly or quickly, and puts pressure on your heart. PPT Thoracic Trauma PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5640397.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cardiac tamponade is an uncommon problem in a district general hospital. Chest pain radiating to your neck, shoulders, or back. Cardiac tamponade is the accumulation of excess fluid within the pericardial space, resulting in impaired cardiac filling, reduction in stroke volume, and epicardial coronary artery compression with resultant myocardial ischemia. Manage your other health conditions: Cardiac tamponade.
 Source: escardio.org
Source: escardio.org
The management of pericardial disease is often simple and rewarding, but. This pressure keeps the ventricles of the heart from expanding fully, making the heart not able to work the right way. Cardiac tamponade can appear acutely, or it may develop rather gradually. The best treatments for a confirmed tamponade are iv fluids and pericardiocentesis. Triage strategy for urgent management of cardiac tamponade.
 Source: osmosis.org
Source: osmosis.org
Triage strategy for urgent management of cardiac tamponade: Factors that influence the management strategy include evaluating the cause, providing haemodynamic support, and. Because of the pressure, your heart can’t beat correctly, causing a drop in blood pressure. This results in “bowing” of the intraventricular septum into the left ventricle causing a reduction in left ventricular filling. Pericardial Tamponade What Is It, Causes, Pericardial Effusion, Signs.
 Source: myamericannurse.com
Source: myamericannurse.com
Cardiac tamponade is an emergency, and definitive therapy is fluid removal by pericardiocentesis. Cardiac tamponade happens when the space around your heart fills with blood or other fluid, putting pressure on your heart. Prompt diagnosis is key to reducing the mortality risk in patients with tamponade. The condition is a medical emergency, the complications of. Acute cardiac tamponade American Nurse.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
This fluid quickly compresses the heart, preventing it from adequately pumping blood because it cannot fill properly. Symptoms vary depending on the acuteness of presentation and on the underlying cause. Published online by cambridge university press: Ut southwestern’s skilled heart doctors use a variety of. Cardiac tamponade.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cardiac tamponade can appear acutely, or it may develop rather gradually. The condition is confirmed with an echo. The condition is a medical emergency, the complications of. Management of cardiac tamponade after cardiac surgery. Cardiac tamponade.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
When the ventricles are not allowed to fill as they want, we see a decrease in stroke volume, a drop in cardiac output, and visible signs of shock. Their case histories are presented and the management in the light of these described. A position statement of the european society of cardiology working group on myocardial and pericardial diseases.eur heart j 2014; Management of cardiac tamponade after cardiac surgery. PPT Chest Trauma, Chest Tubes & Underwater Seal Drainage PowerPoint.
 Source: gokuyute.blogspot.com
Source: gokuyute.blogspot.com
Cardiac tamponade is a cardiac emergency and can be fatal if it is not quickly diagnosed and treated promptly. Factors that influence the management strategy include evaluating the cause, providing haemodynamic support, and. Cardiac tamponade is the accumulation of excess fluid within the pericardial space, resulting in impaired cardiac filling, reduction in stroke volume, and epicardial coronary artery compression with resultant myocardial ischemia. Cardiac tamponade is a fluid buildup around the heart that constitutes a medical emergency. Cardiac Tamponade Nursing Diagnosis / PPT Cardiac Tamponade Overview.
 Source: rnpedia.com
Source: rnpedia.com
Prompt diagnosis is key to reducing the mortality risk in patients with tamponade. Commentary based on ristic ad, imazio m, adler y, et al. The management of pericardial disease is often simple and rewarding, but. Learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment of cardiac tamponade. Cardiac Tamponade Nursing Care Plan & Management RNpedia.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
This makes it difficult for your heart to pump. Clinical sings of cardiac tamponade depends on the rapidity of the fluid accumulation and on the fluid. Factors that influence the management strategy include evaluating the cause, providing haemodynamic support, and. This concept is seen clinically in the form of “pulsus paradoxus.”. Cardiac tamponade BY PANKAJ.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The fluid that causes tamponade is usually either a typical pericardial effusion (that is, the accumulation of an abnormal amount of fluid in the pericardial sac) or bleeding into the pericardial sac. Symptoms vary depending on the acuteness of presentation and on the underlying cause. Cardiac tamponade happens when the space around your heart fills with blood or other fluid, putting pressure on your heart. Cardiac tamponade is the accumulation of excess fluid within the pericardial space, resulting in impaired cardiac filling, reduction in stroke volume, and epicardial coronary artery compression with resultant myocardial ischemia. Cardiac tamponade.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cardiac tamponade is an emergency, and definitive therapy is fluid removal by pericardiocentesis. This pressure keeps the ventricles of the heart from expanding fully, making the heart not able to work the right way. The cardiac tamponade triad presents with hypotension, a narrow pulse pressure, jvd, muffled heart sounds and potentially pulsus paradoxus. In certain conditions, fluid removal is still the optimal choice, but a conservative approach using haemodialysis may be employed. Cardiac tamponadePericardial Effusion….
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cardiac tamponade is a health problem affecting the heart. Severe cardiac tamponade sometimes causes very low blood pressure. In cardiac tamponade, the right ventricular free wall is constricted by the pericardial effusion. Some of the symptoms of cardiac tamponade might look like other health problems. Pericardial Tamponade.
 Source: aetcm.in
Source: aetcm.in
Commentary based on ristic ad, imazio m, adler y, et al. Cardiac tamponade is a health problem affecting the heart. Cardiac tamponade is a clinical syndrome caused by the accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space, resulting in reduced ventricular filling and subsequent hemodynamic compromise. Cardiac tamponade is a fluid buildup around the heart that constitutes a medical emergency. Cardiac Tamponade.
 Source: baronerocks.com
Source: baronerocks.com
This makes it difficult for your heart to pump. In either case, symptoms are usually quite striking, and the resolution of symptoms requires the. The condition is confirmed with an echo. Cardiac tamponade is a cardiac emergency and can be fatal if not diagnosed and treated quickly.anyone who experiences an acute onset of chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, and a feeling of drowsiness should call 911 immediately. Cardiac Tamponade.
The Management Of Pericardial Disease Is Often Simple And Rewarding, But.
Published online by cambridge university press: Cardiac tamponade is a buildup of fluid in the pericardial sac that surrounds the heart which impairs the heart’s ability to contract and the ventricles to fill normally. Management of cardiac tamponade after cardiac surgery. Trouble breathing or taking deep.
Cardiac Tamponade Is An Uncommon Problem In A District General Hospital.
Clinical sings of cardiac tamponade depends on the rapidity of the fluid accumulation and on the fluid. The best treatments for a confirmed tamponade are iv fluids and pericardiocentesis. If not treated, it is always fatal. Cardiac tamponade is a clinical syndrome caused by the accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space, resulting in reduced ventricular filling and subsequent hemodynamic compromise.
This Makes It Difficult For Your Heart To Pump.
This results in “bowing” of the intraventricular septum into the left ventricle causing a reduction in left ventricular filling. Cardiac tamponade can appear acutely, or it may develop rather gradually. A position statement of the european society of cardiology working group on myocardial and pericardial diseases.eur heart j 2014; Blood or fluid collects in the pericardium (the sac that surrounds the heart).
Ut Southwestern’s Skilled Heart Doctors Use A Variety Of.
This pressure keeps the ventricles of the heart from expanding fully, making the heart not able to work the right way. In adults, cardiac tamponade appears to be slightly more common in men than in women. The fluid may collect slowly or quickly, and puts pressure on your heart. The fluid that causes tamponade is usually either a typical pericardial effusion (that is, the accumulation of an abnormal amount of fluid in the pericardial sac) or bleeding into the pericardial sac.







