There is a major difference in cardiac output between trained and untrained individuals performing endurance activities. Heart rate x stroke volume =cardiac output for a given cardiac output, defining a tissue perfusion requirement, an increase in the stroke volume reduces the heart rate, and a decrease in stroke volume leads to a rise in the heart rate.
, Your stroke volume increases during exercise but reaches a plateau, as there is a. The heart rate increases because of a decrease in parasympathetic activity of sa node.
 Learn InfraSonic Monitoring Inc. From ism.care
Learn InfraSonic Monitoring Inc. From ism.care
Heart rate x stroke volume =cardiac output for a given cardiac output, defining a tissue perfusion requirement, an increase in the stroke volume reduces the heart rate, and a decrease in stroke volume leads to a rise in the heart rate. This is illustrated in the adjacent graph, showing how the heart rate increases to match the. This increase in blood flow increases the amount of oxygen being delivered each minute to the muscle that is working. Factors affect cardiac output by changing.
Learn InfraSonic Monitoring Inc. However, if the heart rate increases so much to the.
The effect of exercise on cardiac output, with the consistent conclusion that exercise can significantly affect cardiac output, particularly during high intensity exercise bouts. So cardiac output is quite simply the product of heart rate and stroke volume. Therefore, cardiac output rises during exercise due to increased stroke volume and heart rate. There is a major difference in cardiac output between trained and untrained individuals performing endurance activities.
 Source: ism.care
Source: ism.care
The cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volume. Generally, the resting cardiac output is about 5 liters per. During exercise, the cardiac output increases more than the total resistance decreases, so the mean arterial pressure usually increases by a small amount. The effect of exercise on cardiac output, with the consistent conclusion that exercise can significantly affect cardiac output, particularly during high intensity exercise bouts. Learn InfraSonic Monitoring Inc..
 Source: physiologicalresponsestotraining.weebly.com
Source: physiologicalresponsestotraining.weebly.com
When stroke volume decreases what maintains cardiac output? Contractility describes the relative ability of the heart to eject a stroke volume (sv) at a given prevailing afterload. Heart rate increases in a linear fashion to increases in the intensity of exercise.; A person’s maximal heart rate will increase or reduce depending on how these factors change daily. Stroke Volume and Cardiac Output Physiological Adaptations In.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Changes in cardiac output that are called for by physiologic conditions can be produced by changes in heart rate or stroke volume or both. Expressed as beats per minute or bpm) [76]. Pulse pressure, in contrast, markedly increases because of an increase in both stroke volume and the speed at which the stroke volume is ejected.in addition, working muscles increase stroke. The “american council on exercise’s personal trainer manual” lists exercise adaptations as increased ventricle size, decreased exercise heart rate and increased stroke volume. Relation between individual stroke volume and heart rate in all.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Stroke volume refers to the amount of blood that is ejected by the heart with each beat.; The heart rate has a direct effect on the cardiac output, if increases, the. Therefore, cardiac output rises during exercise due to increased stroke volume and heart rate. Cardiac output can be calculated by multiplying stroke volume, or the amount of blood your heart pumps with each beat, times the number of times it beats per minute, or your heart rate. Heart rate, stroke volume, cardiac output and onelegged blood flow.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Therefore, cardiac output rises during exercise due to increased stroke volume and heart rate. When stroke volume decreases the body attempts to maintain adequate cardiac output by increasing the rate and strength of cardiac contraction. Cardiac output (co) is the blood volume the heart pumps through the systemic circulation over a period measured in liters per minute.[1][2] there are various parameters utilized to assess cardiac output comprehensively, but one of the more. The extra time for filling results in a higher stroke volume, or amount of blood that can be pumped in one beat. what effects blood volume How Are Cardiac Output And Stroke Volume.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Increase in cardiac output is due primarily to an increase in heart. To understand the principles of cardiac stroke volume (sv), it is necessary first to define the concept of cardiac output. The extra time for filling results in a higher stroke volume, or amount of blood that can be pumped in one beat. Increasing either heart rate or stroke volume increases cardiac output. Heart rate (Panel A), stroke volume (Panel B), cardiac output (Panel C.
 Source: deltexmedical.com
Source: deltexmedical.com
This increase in blood flow increases the amount of oxygen being delivered each minute to the muscle that is working. The cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volume. Pulse pressure, in contrast, markedly increases because of an increase in both stroke volume and the speed at which the stroke volume is ejected.in addition, working muscles increase stroke. A stroke volume of 100/minute and a heart rate of 50/minute would yield an acceptable cardiac output of 5 litres. Stroke Volume and Cardiac Output.
 Source: differencebetween.com
Source: differencebetween.com
Because it depends on both volume and amount of time, cardiac output is a rate expressed as liters per. The volume of blood ejected from the heart in a single beat) and heart rate (hr; Stroke volume and cardiac output are responsible for the blood flow around the body. If you train it, it will get bigger and stronger (hypertrophy), increasing the resting stroke volume. Difference Between Stroke Volume and Cardiac Output Compare the.
 Source: ecgwaves.com
Source: ecgwaves.com
The effect of exercise on cardiac output, with the consistent conclusion that exercise can significantly affect cardiac output, particularly during high intensity exercise bouts. Stroke volume increases with physical activity because your exercising muscles need more oxygen and nourishment, which are both received from the blood. Pulse pressure, in contrast, markedly increases because of an increase in both stroke volume and the speed at which the stroke volume is ejected.in addition, working muscles increase stroke. Factors affect cardiac output by changing. Exercise physiology from normal response to myocardial ischemia.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This is illustrated in the adjacent graph, showing how the heart rate increases to match the. Increase in cardiac output is due primarily to an increase in heart. Contractility describes the relative ability of the heart to eject a stroke volume (sv) at a given prevailing afterload. Cardiac output increases in a linear fashion to increases in the intensity of exercise, up to the point of exhaustion. Cardiac Output Cardiac, Cardiac nursing, Cardiac anatomy.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Cardiac output (co) is the blood volume the heart pumps through the systemic circulation over a period measured in liters per minute.[1][2] there are various parameters utilized to assess cardiac output comprehensively, but one of the more. The “american council on exercise’s personal trainer manual” lists exercise adaptations as increased ventricle size, decreased exercise heart rate and increased stroke volume. During exercise, the cardiac output increases more than the total resistance decreases, so the mean arterial pressure usually increases by a small amount. The heart rate has a direct effect on the cardiac output, if increases, the. Solved Below Is Illustration A Cardiac Pressurevolume Cu….
 Source: triagemethod.com
Source: triagemethod.com
It is the product of stroke volume (sv; Stroke volume and cardiac output are responsible for the blood flow around the body. Cardiac output is a function of heart rate and stroke volume [75]. Therefore, cardiac output rises during exercise due to increased stroke volume and heart rate. Cardiac Output, Blood Pressure & Exercise Cardiovascular Physiology.
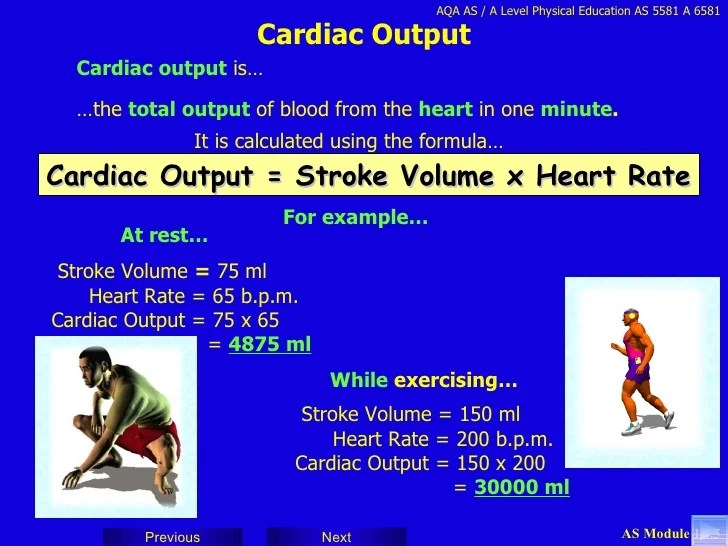 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
In addition, working muscles increase stroke volume by sending higher amounts of blood volume back towards the lungs for oxygen. When stroke volume decreases what maintains cardiac output? The most important control of heart rate and strength of contraction is autonomic innervation. The heart is a muscle just like any other (kind of). PEShare.co.uk Shared Resource.
 Source: basicmedicalkey.com
Source: basicmedicalkey.com
This increases the workloads within the If you train it, it will get bigger and stronger (hypertrophy), increasing the resting stroke volume. Stroke volume refers to the amount of blood that is ejected by the heart with each beat.; In addition, working muscles increase stroke volume by sending higher amounts of blood volume back towards the lungs for oxygen. Cardiovascular System Disorders Basicmedical Key.
 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
Myocardial infarction and/or congestive heart failure) may have a low stroke volume. Therefore, your heart can maintain a high cardiac output with less effort. Expressed as beats per minute or bpm) [76]. Your stroke volume increases during exercise but reaches a plateau, as there is a. 19.4 Cardiac Physiology Anatomy and Physiology.
 Source: austincc.edu
Source: austincc.edu
Output increase is due to a large increase in heart rate and a small increase in stroke volume. Heart rate increases in a linear fashion to increases in the intensity of exercise.; The effect of exercise on cardiac output, with the consistent conclusion that exercise can significantly affect cardiac output, particularly during high intensity exercise bouts. This is illustrated in the adjacent graph, showing how the heart rate increases to match the. Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review.
 Source: polar.com
Source: polar.com
Training results in an increase in stroke volume and cardiac output, which increased blood flow. Most improvement to cardiac output is contributed to increased stroke volume. Healthy individuals with higher cardiovascular fitness levels have lower heart rates, allowing a longer time for the heart to fill with blood. Your stroke volume increases during exercise but reaches a plateau, as there is a. What Is Cardiac Drift And How It Affects Your Training Polar Blog.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volume. Cardiac output (co) is the blood volume the heart pumps through the systemic circulation over a period measured in liters per minute.[1][2] there are various parameters utilized to assess cardiac output comprehensively, but one of the more. Changes in cardiac output that are called for by physiologic conditions can be produced by changes in heart rate or stroke volume or both. The mean cardiac output during exercise have been obtained. Diff'rent strokes on Pinterest.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
However, if the heart rate increases so much to the. Training results in an increase in stroke volume and cardiac output, which increased blood flow. The heart rate increases because of a decrease in parasympathetic activity of sa node. Stroke volume refers to the amount of blood that is ejected by the heart with each beat.; Cardiac output.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Increase in cardiac output is due primarily to an increase in heart. Heart rate x stroke volume =cardiac output for a given cardiac output, defining a tissue perfusion requirement, an increase in the stroke volume reduces the heart rate, and a decrease in stroke volume leads to a rise in the heart rate. Cardiac output is measured by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume. On the other side of the continuum, patients with a significant cardiac history (i.e. Cardiac Physiology Anatomy and Physiology II.
 Source: anotmychapter11.weebly.com
Source: anotmychapter11.weebly.com
This increase in blood flow increases the amount of oxygen being delivered each minute to the muscle that is working. The heart rate increases because of a decrease in parasympathetic activity of sa node. Cardiac output is the measurement of blood that is pumped by the heart in a single minute. Cardiac output can be calculated by multiplying stroke volume, or the amount of blood your heart pumps with each beat, times the number of times it beats per minute, or your heart rate. Cardiac Output Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System.
 Source: pdhpe.net
Source: pdhpe.net
Cardiac output is the measurement of blood that is pumped by the heart in a single minute. A stroke volume of 100/minute and a heart rate of 50/minute would yield an acceptable cardiac output of 5 litres. The cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volume. Most improvement to cardiac output is contributed to increased stroke volume. Stroke volume HSC PDHPE.
 Source: trainerize.me
Source: trainerize.me
Heart rate increases in a linear fashion to increases in the intensity of exercise.; Cardiac output is measured by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume. Cardiac output is the measurement of blood that is pumped by the heart in a single minute. Myocardial infarction and/or congestive heart failure) may have a low stroke volume. "Cardio" Part 1 Why LowIntensity Matters Trainerize.me.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Trained athletes generally have a. Cardiac output (co) is the blood volume the heart pumps through the systemic circulation over a period measured in liters per minute.[1][2] there are various parameters utilized to assess cardiac output comprehensively, but one of the more. In addition, working muscles increase stroke volume by sending higher amounts of blood volume back towards the lungs for oxygen. Output increase is due to a large increase in heart rate and a small increase in stroke volume. Cardiovascular physiology for anesthesia.
 Source: benthamopen.com
Source: benthamopen.com
Because it depends on both volume and amount of time, cardiac output is a rate expressed as liters per. Stroke volume refers to the amount of blood that is ejected by the heart with each beat.; The heart rate increases because of a decrease in parasympathetic activity of sa node. Cardiac output is measured by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume. Does Stroke Volume Increase During an Incremental Exercise? A.
Generally, The Resting Cardiac Output Is About 5 Liters Per.
During exercise, the cardiac output increases more than the total resistance decreases, so the mean arterial pressure usually increases by a small amount. To understand the principles of cardiac stroke volume (sv), it is necessary first to define the concept of cardiac output. In addition, working muscles increase stroke volume by sending higher amounts of blood volume back towards the lungs for oxygen. Cardiac output is measured by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume.
The Cardiac Output = Heart Rate X Stroke Volume.
During exercise, the cardiac output increases more than the total resistance decreases, so the mean arterial pressure usually increases by a small amount. At the onset of exercise your muscles signal your heart to pump faster for increased blood flow. Trained athletes generally have a. Changes in cardiac output that are called for by physiologic conditions can be produced by changes in heart rate or stroke volume or both.
Healthy Individuals With Higher Cardiovascular Fitness Levels Have Lower Heart Rates, Allowing A Longer Time For The Heart To Fill With Blood.
There is a major difference in cardiac output between trained and untrained individuals performing endurance activities. The heart rate has a direct effect on the cardiac output, if increases, the. Heart rate x stroke volume =cardiac output for a given cardiac output, defining a tissue perfusion requirement, an increase in the stroke volume reduces the heart rate, and a decrease in stroke volume leads to a rise in the heart rate. Therefore, cardiac output rises during exercise due to increased stroke volume and heart rate.
The Effect Of Exercise On Cardiac Output, With The Consistent Conclusion That Exercise Can Significantly Affect Cardiac Output, Particularly During High Intensity Exercise Bouts.
Output increase is due to a large increase in heart rate and a small increase in stroke volume. Expressed as beats per minute or bpm) [76]. The volume of blood ejected from the heart in a single beat) and heart rate (hr; Changes in cardiac output that are called for by physiologic conditions can be produced by changes in heart rate or stroke volume or both.







